Case study:
Disinfection testing on living human skin
Simultaneous visualization of virus disinfection efficiency and the impact on skin physiology
As an independant laboratory, we were contacted by the company Aquila Bioscience to measure the efficiency of one of their disinfection product on living human skin. This ABD (Anti Bioagent Decontamination) Device works by physically capturing pathogens on both skin and surfaces. Pathogens bind to the solution and are stripped from skin and surfaces in a Velcro-like action. Our goal was to investigate and measure the efficacy of the product before commercial launch.
Note: our experiment on living human skin is conform to the requirements set out by the French Research Ethics Committee respecting the dignity, rights, safety and well-being of the people involved in the study.
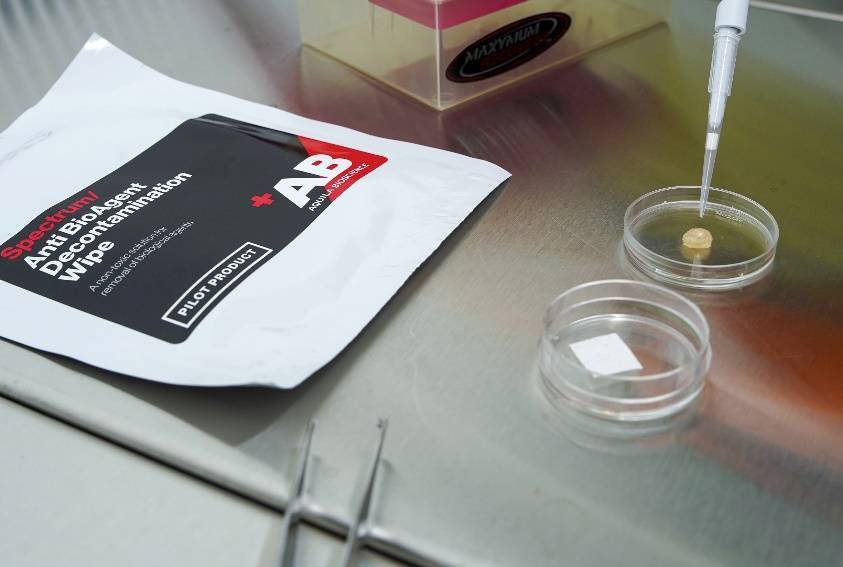
Challenging ABD wipes on SARS-CoV-2 contaminated skin
A prepartation of SARS-CoV-2 virus was deposit on the surface of living human skin explants. A small piece of a control wipe, PBS soaked wipe or ADB wipe was then apply without movement on the skin.
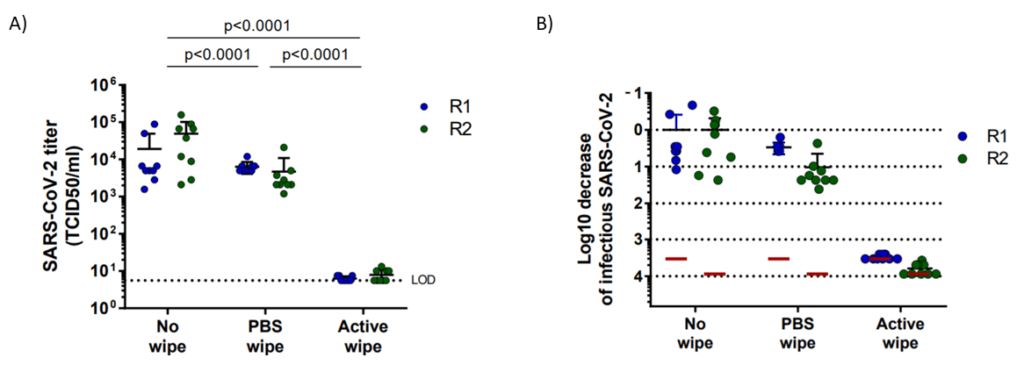
After generation of a full report and a certificate of analysis for Aquila Bioscience customer, Abwipe was launched on the market.


